RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) has traditionally operated as a UDP-based protocol, facilitating communication between clients and servers through attribute-value pairs (AVPs) transmitted as plain text. RADIUS supports various authentication mechanisms, including PAP, PEAP, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, MSCHAP, MSCHAPv2, EAP-MD5, and a few others.
Using the RADIUS PAP protocol over UDP is particularly vulnerable since the User-Password AVP is encrypted using only a shared secret. If an eavesdropper gains access to the shared secret, or is able to guess or brute-force it, they can use it to decrypt the User-Password AVP to gain illegitimate access to the protected device or network.
With protocols like PEAP, EAP-TTLS, MSCHAP, MSCHAPv2, and EAP-MD5, credentials or challenges are transmitted within the EAP protocol using the EAP-Message AVP. Although some EAP protocols require data encryption via TLS (where a server certificate validates the server for encrypted data transfer), the server certificate details in EAP-Message AVP, the User-Name attribute, and other AVPs still get exchanged as plain text, as shown below. This means attackers can obtain server certificate details (C=AU, ST=Some-State, O=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd) and other client information, compromising privacy even if the security remains intact.
UDP-based RADIUS can carry EAP-TLS, a very secure, certificate-based protocol (where both client and server validate each other through certificate exchange), but the protocol's plain text transmission in EAP-Message AVP still allows important server and client certificate details (often including the user's email address) to be visible to eavesdroppers, compromising privacy.
A recently discovered vulnerability for non-EAP-based protocols (PAP, CHAP) further demonstrates UDP-based RADIUS protocol flaws, as attackers can potentially gain network access without knowing the shared secret, as detailed at https://blastradius.fail/attack-details.
It's important to distinguish between a privacy breach and a security breach in this context. A privacy breach occurs when the user details in the transaction become visible to eavesdroppers, while a security breach involves an attacker successfully gaining unauthorized network access—a considerably more severe scenario.
While the most secure UDP-based EAP-TLS protocol still has privacy concerns, RadSec provides comprehensive protection against both privacy and security vulnerabilities.
RadSec represents a significant security improvement by encapsulating the entire RADIUS protocol exchange within a secure TCP tunnel established through mutual TLS. This approach:
Establishes a secure, encrypted tunnel through certificate-based mutual authentication before any data is exchanged, ensuring both client and server verify each other's identity.
Provides persistent mutual TLS-based TCP connections between client and server, offering resistance to packet losses common with UDP
Prevents eavesdropping even when network traffic is intercepted, as the data cannot be decrypted without access to the encryption certificates
Eliminates dependency on a single shared secret for transport security
By providing enhanced protection for the entire protocol exchange, RadSec not only addresses the security concerns comprehensively but also the transport-layer privacy issues present in traditional UDP-based RADIUS implementations, making it a more secure protocol overall.
UDP RADIUS Illustration
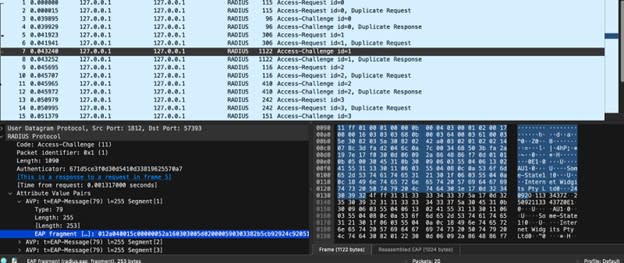
The Wireshark capture below provides a clear demonstration of how UDP-based EAP-TLS RADIUS shows its inherent privacy vulnerabilities. The packet capture reveals multiple RADIUS exchanges between the client and the RADIUS server, showing the complete sequence of Access-Request and Access-Challenge messages with their corresponding packet identifiers.
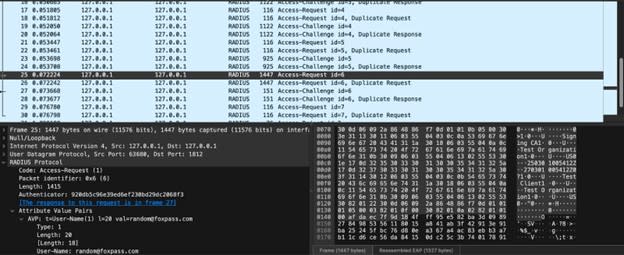
Examining the bottom section of the capture reveals the RADIUS payload, which shows the Attribute Value Pairs (AVPs) containing sensitive authentication information. This includes the User-Name attribute with value "random@foxpass.com" alongside other attributes such as NAS-Identifier and Called-Station-Id. The detailed hex dump on the right displays the raw packet contents transferred using AVPs, clearly exposing username details, server and client certificate details (certificate subject: CN=Test Client, O=Test Organization, C=US)—a significant privacy concern.
This privacy issue, in addition to the security concerns discussed in the above section, is precisely what RadSec was designed to address. By encapsulating these exchanges within a secure TLS tunnel created through mutual certificate validation, RadSec prevents exposure of such sensitive details to potential eavesdroppers. Even RADIUS's least secure authentication mechanism, PAP, is very secure with RadSec.
How RadSec Works
RadSec enhances security by encapsulating traditional RADIUS protocol exchanges within a secure TLS tunnel, ensuring all client-server data transfers remain encrypted. Unlike its UDP-based predecessor, RadSec establishes a persistent TCP connection where both parties authenticate each other through X.509 certificates during a mutual TLS handshake. This robust two-way validation creates an encrypted tunnel before any RADIUS data transmission occurs.
Once this secure channel is established, standard RADIUS packets (Access-Request, Access-Challenge, etc.) travel within this encrypted layer, effectively shielding them from eavesdropping and tampering attempts. The persistent connection is maintained throughout the session, offering significant improvements in both efficiency and security compared to UDP RADIUS's approach, which is prone to packet loss.
With the certificate-based trust model, RadSec eliminates traditional RADIUS's major security weaknesses, i.e., both privacy and security. Typically operating over TCP port 2083 (though this is configurable), RadSec provides comprehensive protection for the entire communication channel. This comprehensive approach makes RadSec highly resistant to packet sniffing, replay attacks, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
RadSec at Foxpass: Global, Scalable, and Low Latency Authentication Infrastructure
We've created RADIUS authentication with a cutting-edge RadSec implementation that’s performant, reliable, and globally accessible.
Our RadSec service is designed to meet the most demanding connectivity requirements across diverse global environments. We’ve created a horizontally scalable, multi-tenant architecture where customers connecting to our servers always connect to the nearest available server.
Global Proximity, Instant Connectivity, Effortless Management
Our global deployment ensures that every customer connects to the nearest RadSec server, dramatically reducing latency and improving response times. Just a single DNS hostname is provided to the customers, but clients automatically connect to the most optimal server based on geographic proximity.
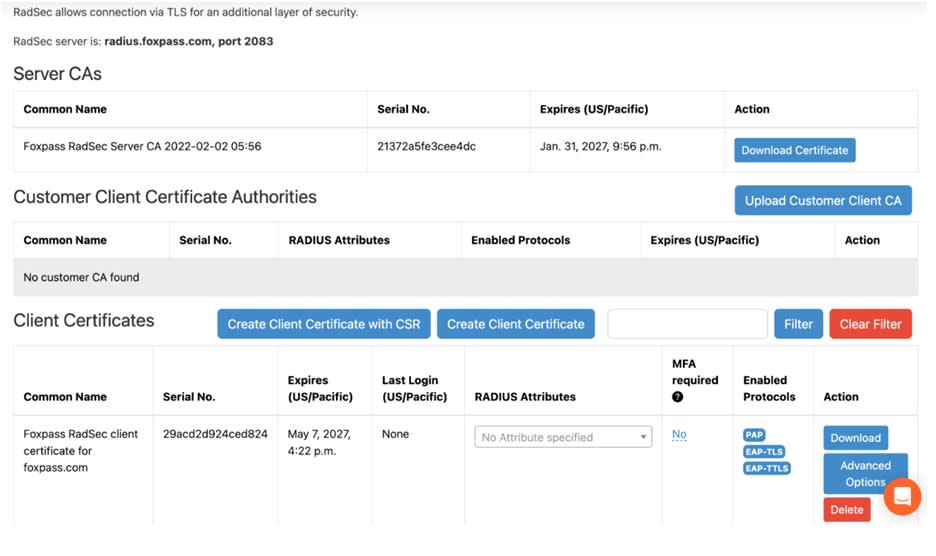
Foxpass's RadSec supports two options for managing client certificates. Either Foxpass can issue certificates from our shared CA, or customers can easily upload their CA certificates through our intuitive console, which quickly propagates these credentials across our entire global server network, ensuring only the authenticated clients gain access.
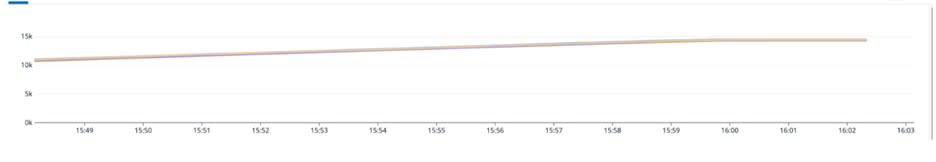
Unprecedented Scale and Performance
Each of our RadSec server instances is engineered to handle over 15,000 simultaneous connections, providing robust, reliable authentication at a scale that meets enterprise-grade demands.
Key Highlights
Horizontally scalable and multi-tenant implementation of RadSec
Global server network with intelligent routing
Massive connection capacity (15,000+ connections per instance)
Seamless, low-latency authentication experience
Get Started with Foxpass Today
Ready to upgrade your authentication security? Foxpass offers enterprise-grade protection, global performance, and zero-hassle deployment. Whether you're securing user credentials or managing certificate-based access at scale, our RadSec implementation ensures your data stays private and protected.
Start your free trial of Foxpass today and experience the difference of a secure, scalable, and modern authentication infrastructure.
Acknowledgments:
We would like to thank the entire team for making this available to our customers across the world.





