When it comes to cloud computing, the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is the foundation of employee directory and user credentials. Whether it’s managing logins for your AWS EC2 instance, your VPN, or your legacy application, LDAP can manage it all.
A build-it-yourself LDAP solution like OpenLDAP can be somewhat difficult to manage, and the required maintenance makes for very tedious work. Although it’s extremely time-consuming overall, cloud LDAP has made a key piece of network security infrastructure readily accessible for any business’ access control needs.
Created in 1993, LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol and is a standard application protocol for accessing and managing a directory service. LDAP was created as a simple implementation of the International Standardization Organization (ISO) X.500 standard for directory services.
LDAP requires very little to get up and running on the client side, which makes it a particularly good choice for networked server applications, otherwise known as “thin client” apps.

Think of LDAP as a gigantic, virtual telephone book. When you open the telephone book, you suddenly have access to a large directory which is the key to thousands of different people’s contact information (their user credentials.)
LDAP houses user credentials in a tree-like structure, naturally called the “Directory Information Tree” (or DIT for short). The top of the tree starts at the Root Distinguished Name, also called the “Naming Context,” or the “Suffix.”
Each position on the LDAP DIT refers to its individual Distinguished Name (DN for short). As an example, user credentials in the DIT can be stored according to host domain, department, and person name.
When you log into the LDAP server in preparation to initiate a search for a user or group, this is called the act of "binding." Essentially, binding is the process of authenticating the user’s password credentials.
The names of the attributes of each user, after binding, are abbreviated into mnemonic strings, such as: “cn” for “common name,” “sn” for “surname,” “c” for “country,” “mail” for “email address,” “ou” for organizational unit, or “dc” for “domain component.”
Any DN at the top of the tree takes precedence over the entry below. Therefore, the DIT can be thought of as a waterfall structure that flows down to form a highly structured hierarchical-ordered directory system.
In fact, the very place in which the DN appears speaks to its schema within the directory, listed between commas and with equal signs syntactically listing search criteria.
An example DN for example.com could look like this:
["uniqueIdentifier=85317,dc=person,s=state,c=us,dc=example,dc=com"]
A full DIT schema may look like this:
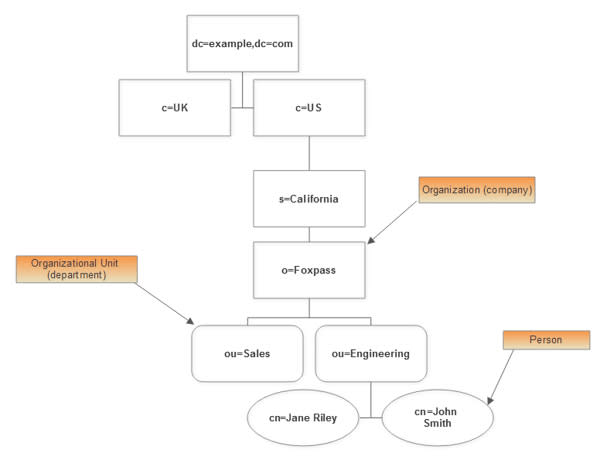
As you can see, LDAP isn’t something you can just pick up and implement for an entire business in a week, or even a month. Manually managing LDAP is often convoluted and highly frustrating. In fact, it was out of that frustration that Foxpass was created!
Foxpass comes packaged within a straightforward dashboard that makes assigning groups and permissions for your employees way easier than OpenLDAP.
With Foxpass, you can implement an easy-to-use Cloud LDAP solution in minutes, not days or weeks. Foxpass makes it easier than ever to manage credentials, access, and security – try it for yourself and see.
Upgrade Your Security
Ready for the latest in access management and network security? Click here to learn how Foxpass can help you avoid costly security mistakes:



