Networking isn’t just for business conferences. Local area networks are vital tools for keeping devices and users connected in a single network, and with the advent of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), business networks have grown even more efficient and powerful.
With that in mind, it’s important to understand what a VLAN is, how it works, and what Foxpass can do to make your VLAN even more efficient and secure.
A local area network (LAN) is a group of network components that share the same physical network. Therefore, a VLAN is a subnetwork that virtually connects network components of different LANs into a single network, thus circumventing the physical limitations of a LAN environment.
With increasing network complexities that exceed the capacity of normal LANs, VLANs have become an alternative that makes networks flexible, scalable, secure, and fast.
What are the types of VLANs?
There are three basic types of commonly used VLANs:
Protocol VLAN: Protocol VLANs handle traffic based on the protocols that they use. Switches separate and forward traffic based on the protocol over which the VLAN is deployed. Traffic of other protocols is not forwarded to the port.
Static VLAN: Static VLAN is also known as a port-based VLAN. In this type of VLAN, the network administrators assign ports on a network switch to a particular virtual network.
Dynamic VLAN: As opposed to static VLANs, dynamic VLANs allow network administrators to define network membership based on the characteristics of devices.
How does VLAN work?
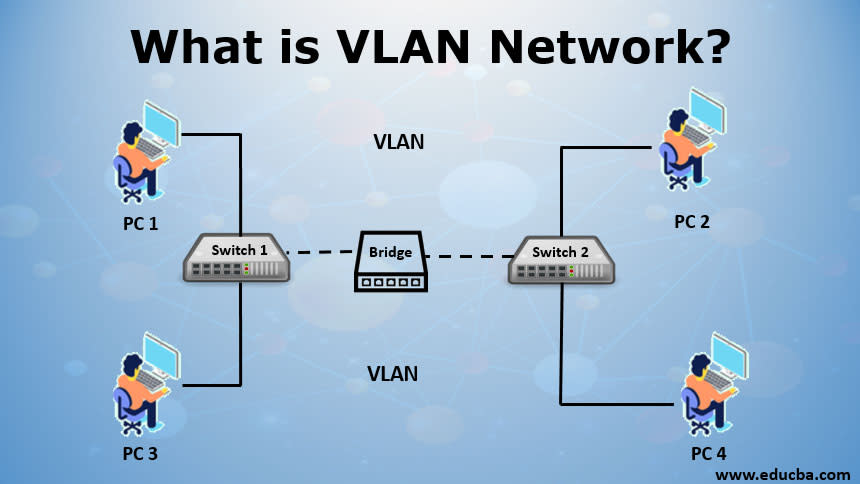
VLANs divide a single physical LAN into multiple logical network segments. These logical network segments then communicate with each other as if they were comprised of a single LAN, when in reality they exist on one or more LANs.
The network segments are separated from the rest of the physical LAN using a router, switch, or bridge. As such, when a network node broadcasts data, it reaches other nodes of a VLAN but not on other segments of the physical LAN.
When a LAN bridge receives data from a network node, the data is tagged either explicitly or implicitly. Explicit tagging occurs when a VLAN identifier is attached to the data, so it becomes easier for the bridge to determine the next node for the data. Implicit tagging occurs by utilizing the information present in the data (for instance, the port on which the data arrived).
Based on implicit or explicit tagging, the bridge determines where the data needs to be routed to, sends the data to the next node, and isolates the particular LAN segment from the rest of the LAN.
Why use a VLAN?
VLANs simplify the complexities that are inherent in physical LANs. In a simple physical LAN, when two nodes send traffic at the same time, the data is not transmitted to the destination properly because of a collision. This collision renders the entire LAN busy, and the original data has to be sent again.
VLANs, on the other hand, transmit data from one segment to another using a switch or bridge, reducing the chances of collisions and instead of broadcasting the data to all connected network devices. Apart from this, there are other benefits of using a VLAN:
Cost-effectiveness
VLANs communicate through switches and do not require routers unless they are sending data outside the VLAN. As a result, VLANs can manage additional data load, decrease data latency, and ultimately reduce costs.
Flexibility
VLANs can be port-based, protocol-based, or subnet-based, making for a flexible networking arrangement that can be configured between different buildings or floors, regardless of proximity to other network nodes.
Decreased administrative oversight
VLANs also free up network administrators’ time, as they divide workstations into different LAN segments. Administrators do not need to reconfigure the network when moving their workstations and can also limit access to users because of the isolation of different LAN segments.
What are the use cases of a VLAN?
Large Companies
Large companies generally deploy a Wide Area Network (WAN) to accommodate the needs of their expansive offices and teams. Having multiple VLANs as an alternative can allow for ease of configuration, cross-functional work, and data sharing between different departments within the company.
Isolation
VLANs can also be used to give guest users access to wireless internet, without even accessing the core organizational network.
Prioritization
Critical traffic can be given more priority over the rest of the network by using and deploying VLAN-based policies.
VoIP
VLANs can also be used to create a logically separate layer for VoIP. This separates the voice network from the other networks, so the voice network typically does not touch the traffic of the underlying network and can be transmitted from one node to another unaltered.
How can Foxpass help?
There are several perceived benefits of using VLANs, but with Foxpass, those benefits can multiply exponentially. Foxpass is a solution that allows you to reap the benefits of VLAN in conjunction with different user access management tools, providing greater security and ease of access across your organization.
Foxpass is an out-of-the-box server and network automation tool that reduces the risk of security breaches by protecting the most sensitive parts of your infrastructure. Foxpass is both scalable and fault–tolerant, making it a powerful solution for businesses of all sizes.
You can use Foxpass to easily integrate VLAN via RADIUS attributes. You can also configure Cisco switches with wireless 802.1x VLAN assignment using Foxpass’s easy-to-use interface, making it easier for you to reap the benefits of using VLAN with proper access management tools like RADIUS.
With the security benefits offered by VLAN environments and the security features provided by Foxpass, you’re sure to have a hardened security infrastructure that keeps security breaches at bay.





